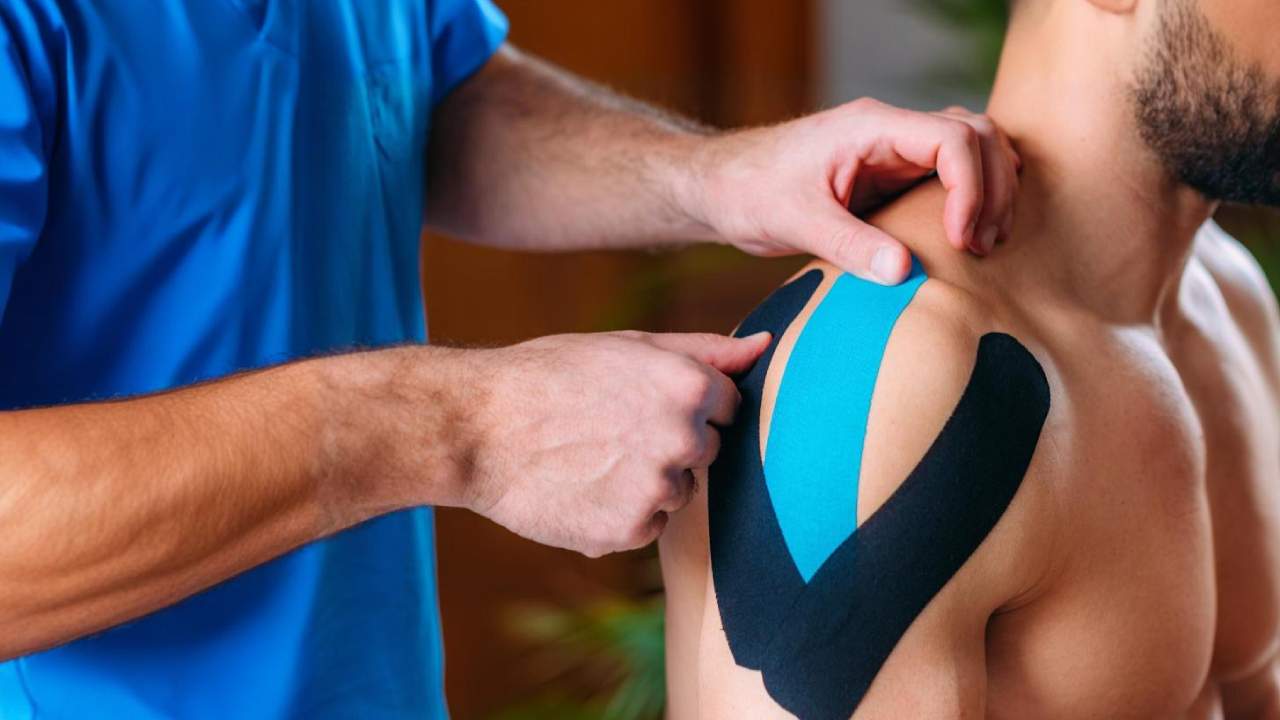
Taping in Hamilton
Taping in Hamilton is a widely used technique in physiotherapy, applied to support joints, muscles, and soft tissues during movement and recovery. It serves as a valuable tool to enhance stability, reduce strain, and improve overall function, making it beneficial for individuals recovering from injuries or managing chronic conditions.
Types of Taping in Physiotherapy
- Rigid Taping: Rigid taping, commonly known as athletic or sports taping, is used to restrict excessive joint movement. This method provides external support to injured ligaments or joints, helping to prevent further strain. It is frequently used in cases of ankle sprains, knee instability, and shoulder injuries. The tape is typically made of non-elastic material, which helps stabilize the joint and reduce unwanted motion.
- Kinesiology Taping: Kinesiology taping involves the use of elastic tape designed to mimic the natural movement of the skin and muscles. This technique allows for a greater range of motion while still providing support. Kinesiology tape is often applied to reduce swelling, improve circulation, and aid in muscle function. Unlike rigid taping, this method does not overly restrict movement, making it suitable for sports and daily activities.
- Dynamic Taping: Dynamic taping is another elastic taping method that focuses on biomechanical correction. This technique provides resistance and assistance to specific movements, helping in movement retraining. It is commonly used in rehabilitation settings to address conditions such as tendon injuries or postural imbalances.
- McConnell Taping: McConnell taping is a technique that involves the use of rigid tape to correct patellar tracking issues and joint alignment problems. It is often applied to address conditions such as patellofemoral pain syndrome and shoulder instability. This method helps to alter joint mechanics, reduce pain, and improve functional movement patterns.
Benefits of Taping in Physiotherapy
- Pain Reduction: Taping in Hamilton can help reduce pain by providing external support to muscles and joints. It can offload stress from injured or overworked tissues, allowing them to recover more effectively. Additionally, certain taping techniques stimulate sensory receptors in the skin, which can help modulate pain perception.
- Enhanced Joint Stability: Individuals recovering from injuries often experience joint instability, which can increase the risk of re-injury. Taping provides structural support that reinforces proper joint alignment and function, helping individuals regain confidence in movement.
- Improved Muscle Function: Certain taping methods, particularly kinesiology taping, are designed to facilitate or inhibit muscle activation. This can be beneficial for individuals with neuromuscular imbalances, muscle weakness, or overactive muscles. By guiding movement patterns, taping can contribute to better muscle coordination and efficiency.
- Swelling and Circulation Management: Kinesiology taping is commonly used to reduce swelling and improve circulation. The tape’s elasticity gently lifts the skin, creating space for lymphatic drainage and improved blood flow. This can be particularly helpful after acute injuries, surgeries, or for individuals dealing with chronic swelling issues.
- Postural Correction: Taping in Hamilton can be utilized to address postural imbalances by providing feedback to the body about alignment and positioning. This is often used in cases of rounded shoulders, excessive spinal curvature, or muscle imbalances that contribute to poor posture. By reinforcing correct movement patterns, taping can support long-term postural improvements.
Common Conditions Treated with Taping
- Sports Injuries: Athletes frequently rely on taping techniques to manage and prevent injuries. Whether it’s an ankle sprain, knee instability, or a strained muscle, taping helps support the affected area without limiting performance excessively. Many athletes use taping as a precautionary measure to reduce the risk of injury recurrence.
- Tendonitis and Overuse Injuries: Repetitive strain injuries, such as tennis elbow or Achilles tendonitis, benefit from taping as it helps offload stress from the affected tendons. This reduces irritation and allows the tissue to recover while maintaining functional mobility.
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation: Taping in Hamilton is often incorporated into post-surgical rehabilitation programs to support healing tissues, manage swelling, and aid in restoring movement. It provides a non-invasive method to assist in the recovery process while reducing the need for external braces or splints in some cases.
- Neurological Conditions: In cases of neurological impairments such as stroke or cerebral palsy, taping is used to facilitate muscle activation and improve movement control. It can assist in stabilizing weak muscles and guiding proper motor patterns, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with movement dysfunctions.
Application Techniques and Considerations
Proper application of taping is essential to achieve the desired benefits. Physiotherapists assess the individual’s condition, movement patterns, and specific needs before applying tape. Some key considerations include:
- Skin Preparation: The skin should be clean and dry before applying tape to ensure optimal adhesion. If necessary, hair may be trimmed to improve tape contact.
- Tension Control: The amount of stretch applied to the tape varies depending on the goal. Too much tension may cause discomfort, while too little may not provide adequate support.
- Duration of Use: Taping should not be worn for extended periods without assessment. Most tapes are designed to last for a few days, but they should be removed if irritation or discomfort occurs.
- Proper Removal: Taping should be removed gently to avoid skin irritation. Using adhesive removers or warm water can help ease the process without causing damage to the skin.
Taping in Hamilton remains a valuable technique in physiotherapy, providing support, pain management, and movement assistance for various conditions. With proper assessment and application, it plays a significant role in rehabilitation and injury prevention.